Django is a Python-based framework that lets you build powerful websites quickly and easily. This article shows how to install and configure a Django demo app on a Linux shared web hosting account that uses cPanel. This demo application uses a SQLite database.
Note that you can install a newer version of SQLite if needed:
How to install latest SQLite version on cPanel
1. Log into your cPanel account

2. Create a Python application
a) Create a new application
![]()
b) Enter application informations
For the demo project, use version 3.11.x
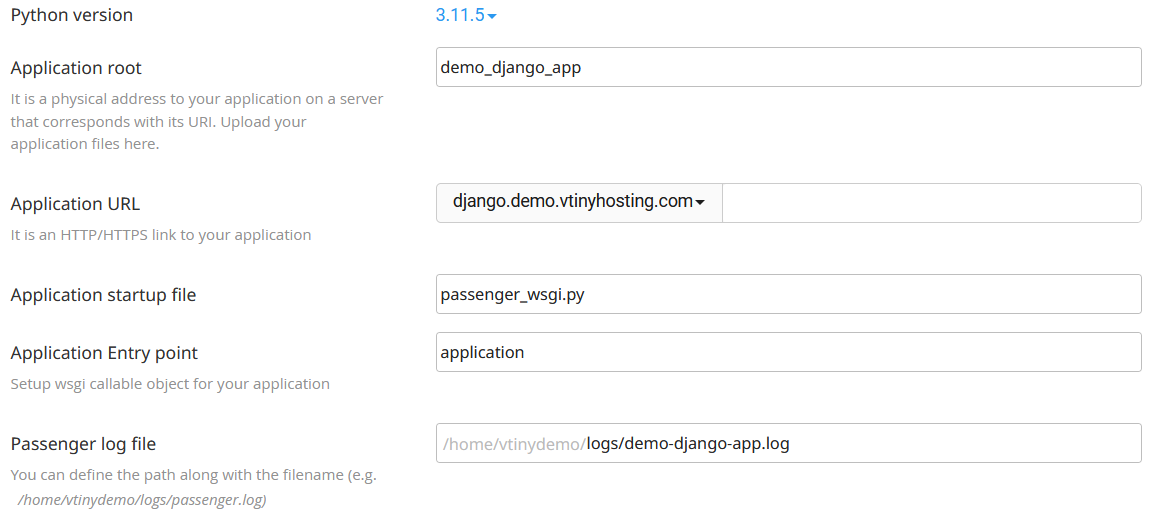

c) Confirm informations
![]()
d) Copy the command that will allow access to the virtual environment
Once the creation of the application is complete, a message is displayed at the top of the screen. Copy the command, you will need it later.
source /home/[your_user]/virtualenv/demo_django_app/[python_version]/bin/activate && cd /home/[your_user]/demo_django_app
3. Configure the Django project
a) Use Terminal or connect with SSH
![]()
![]()
b) Activate the virtual environment
Use the command copied previously. You can return to the settings of your Python application to find the command.
$ source /home/[your_user]/virtualenv/demo_django_app/[python_version]/bin/activate && cd /home/[your_user]/demo_django_appc) Update the program "pip"
$ pip install --upgrade pipd) Download and unzip the demo project
$ wget https://demo.vtinyhosting.com/vtiny-django-demo.zip
$ unzip vtiny-django-demo.zip
$ rm vtiny-django-demo.zipe) Create directories for static files
$ mkdir -p templates/static_pages
$ mkdir static_files
$ mkdir static_mediaf) Install the "packages"
$ pip install -r requirements.txtg) Replace the file "passenger_wsgi.py"
$ mv passenger_wsgi.py passenger_wsgi_bkp.py
$ wget https://demo.vtinyhosting.com/passenger_wsgi.zip
$ unzip passenger_wsgi.zip
$ rm passenger_wsgi.zipFor your projects, don't forget to change "demo_project.settings" to the name of your Django project.
$ nano passenger_wsgi.pyThe final content of the file:
import os
import sys
import django.core.handlers.wsgi
from django.core.wsgi import get_wsgi_application
sys.path.append(os.getcwd())
os.environ['DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE'] = 'demo_project.settings'
SCRIPT_NAME = ''
class PassengerPathInfoFix(object):
"""
Sets PATH_INFO from REQUEST_URI because Passenger doesn't provide it.
"""
def __init__(self, app):
self.app = app
def __call__(self, environ, start_response):
from urllib.parse import unquote
environ['SCRIPT_NAME'] = SCRIPT_NAME
request_uri = unquote(environ['REQUEST_URI'])
script_name = unquote(environ.get('SCRIPT_NAME', ''))
offset = request_uri.startswith(script_name) and len(environ['SCRIPT_NAME']) or 0
environ['PATH_INFO'] = request_uri[offset:].split('?', 1)[0]
return self.app(environ, start_response)
application = get_wsgi_application()
application = PassengerPathInfoFix(application)To save the file: Ctrl+O and Enter
To exist the Nano editor: Ctrl+X
h) Create a super user account
This account will allow you to access the Django administration module :
https://[your_url_application]/admin
$ python manage.py createsuperuseri) Collect static files
$ python manage.py collectstaticj) Restart the Python application
4. Test the site
In your browser, enter the url of your application (section 2.b):
https://[your_url_application]
Vtiny Hosting demo link :
https://django.demo.vtinyhosting.com/